Background
What is a database and why do we need it?
A database is an organized collection of data. It is a repository of information that is stored electronically in a computer system. Databases are used to store large amounts of data in a way that is efficient and organized. This allows users to access and manage the data easily.
There are many reasons why we need databases. Some of the most common reasons include:
- To store large amounts of data. Databases can store millions or even billions of records. This makes them ideal for storing data from large applications, such as e-commerce websites, social media platforms, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
- To organize data. Databases store data in a structured way, which makes it easy to find and access the data that you need. This is in contrast to storing data in spreadsheets or documents, which can be difficult to manage and search.
- To protect data. Databases can be used to protect data from unauthorized access. This is done through security features such as user authentication, encryption, and access control.
- To share data. Databases can be used to share data between different users and applications. This makes it easy to collaborate on projects and to integrate different systems.
There are two main types of databases: relational databases and non-relational databases (NoSQL).
- Relational databases are the most common type of database. They store data in tables, which are made up of rows and columns. Each row in a table represents a single record, and each column represents a single field of data. Relational databases are very efficient at storing and querying structured data.
- NoSQL databases are a newer type of database that are designed to store and query unstructured data. NoSQL databases do not use tables like relational databases. Instead, they use different data models, such as key-value pairs, documents, and graphs. NoSQL databases are often used for applications that need to store large amounts of unstructured data, such as social media platforms and big data analytics applications.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between relational and NoSQL databases:
| Feature | Relational databases | NoSQL databases |
|---|---|---|
| Data model | Tables | Key-value pairs, documents, graphs |
| Efficiency | Efficient for structured data | Efficient for unstructured data |
| Scalability | Horizontally scalable | Vertically scalable |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | More flexible |
| Popularity | More popular | Less popular |
The best type of database for a particular application depends on the specific requirements of the application. If the application needs to store and query structured data, then a relational database is a good choice. If the application needs to store and query unstructured data, then a NoSQL database is a good choice.
Querying Language and SQL
A querying language is a language that is used to interact with a database. It allows users to retrieve, update, and delete data from the database. There are many different querying languages, but the most popular one is SQL (Structured Query Language).
We need a querying language because it provides a standardized way to interact with databases. This makes it possible for different applications and users to access and manipulate the same data in a consistent way. Without a querying language, each application would have to have its own way of interacting with the database, which would be very inefficient and error-prone.
Here are some of the benefits of using a querying language:
- Standardization: A querying language provides a standardized way to interact with databases, which makes it possible for different applications and users to access and manipulate the same data in a consistent way.
- Efficiency: A querying language can be used to perform complex queries on large datasets very efficiently. This is because the querying language is designed to be optimized for database operations.
- Flexibility: A querying language is a very flexible tool that can be used to perform a wide variety of operations on databases. This makes it a powerful tool for data analysis and manipulation.
- Security: A querying language can be used to control access to data in a database. This is done through the use of permissions, which can be used to specify who can read, write, and delete data from the database.
Overall, a querying language is an essential tool for working with databases. It provides a standardized way to interact with databases, which makes it possible for different applications and users to access and manipulate the same data in a consistent way. It is also a very efficient and flexible tool that can be used to perform a wide variety of operations on databases.
In addition to the benefits mentioned above, querying languages also provide a number of other advantages, such as:
- Abstraction: Querying languages abstract away the details of how data is stored in the database, which makes it easier for users to work with data.
- Automation: Querying languages can be used to automate tasks, such as data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL). This can save time and improve efficiency.
- Scalability: Querying languages can be used to scale databases to handle large amounts of data. This is important for applications that need to process large datasets.
Overall, querying languages are essential tools for working with databases. They provide a number of advantages that make them valuable for a wide range of applications.
SQL is a standard language for storing, manipulating, and retrieving data in a relational database. You can use SQL to insert, update, delete, and select any rows of data from a database. The syntax is standard for any SQL databases.
Basic Relational Database Diagram
Since SQL database uses structured data to operate, one way to design the data models and their relationship is to draw a diagram. This diagram is called "Database Diagram".
Modeling database
Tables and Columns
From figure 1, the table name is "books". It has 3 columns which are "id", "title", and "description". Each column has a type and column properties. For example, "id" column has a type of serial and PK indicates that it's a primary key of that table.
Relationships
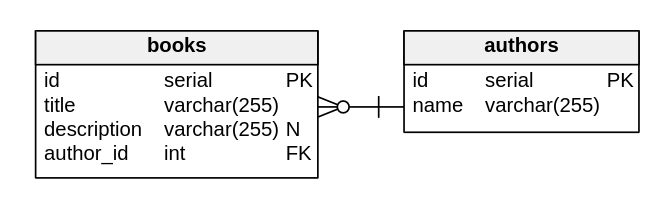
Figure 2: books and authors relationship
Let's assume that a book must have an author. An author may have one or multiple books. Hence, we call a relationship from authors to books as "one-to-many". Therefore, we could model the data as shown in figure 2. From figure 2, the "books" table have a column called "author_id" which links to the "authors" table's "id" field. That indicates that a book may have one and only one author. On the other hand, "authors" may have one or multiple books.
Example Project: Creating a movie reviews database
Concept
We're going to design a movie reviews database. The data model is shown in the diagram below.
Figure 3: Movie and Reviews data model
From figure 3, the relationship between movie and review is one-to-many. Hence, a movie may contain multiple reviews but a review belongs to only one movie.
Object properties
Movie and Review objects have the following properties.
Movie:
- id: An unique identifier of a movie object (integer)
- title: A title of a movie (string)
Review:
- id: An integer unique identifier of a review object (integer)
- stars: A stars rating of a movie from 0 to 5 (integer)
- comment: A comment of the movie review (string)
Database Diagram
From the concept, we could construct a database diagram as the following diagram.
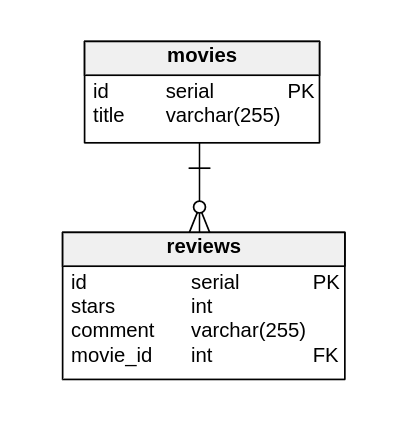
Figure 4: Movie Reviews Database Diagram
From figure 4, there are two tables which are "movies" and "reviews". The "movie" table has two columns which are "id" and "title". The "review" table has four columns which are "id", "stars", "comments", and a "movie_id" column. The "movie_id" column is a foreign key to the "movies" table's primary key column.
To create the tables in SQL, please execute the following snippet.
Installing SQLite3
If you're on Debian system, please execute the following command in install SQLite3.
sudo apt install sqlite3
Creating a database
To create a database using SQLite3, run the following command.
sqlite3 movie_reviews.db
It will create a movie_reviews.db in the current directory. After executing the command, you'll be inside the SQLite console as shown in the following snippet.
Desktop > sqlite3 movie_reviews.db
SQLite version 3.31.1 2020-01-27 19:55:54
Enter ".help" for usage hints.
sqlite>
Creating tables
Once you're inside the console, copy the following snippet to create tables.
-- tables
-- Table: movies
CREATE TABLE movies (
id integer NOT NULL CONSTRAINT movies_pk PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
title varchar(255) NOT NULL
);
-- Table: reviews
CREATE TABLE reviews (
id integer NOT NULL CONSTRAINT reviews_pk PRIMARY KEY,
stars int NOT NULL,
comment varchar(255) NOT NULL,
movie_id int NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT reviews_movies FOREIGN KEY (movie_id)
REFERENCES movies (id)
);
-- End of file.
After that, execute .tables in the console to see list of all tables. You should be able to see movies and reviews tables.
Basic Querying
This guide will walk you through how to insert, update, delete, and select data rows from the database.
Inserting a new movie
To insert a movie, run the following command.
INSERT INTO movies ("title") VALUES ('Spider-Man: Into the Spider-Verse');
The command inserts one movie entry. You can see that we don't have to specify the "id" field because it is auto-generated by SQLite.
You can try inserting multiple values at once. See the following command as an example.
INSERT INTO movies ("title") VALUES
('The amazing spider-man'),
('Spider-Man: Homecoming'),
('Spider-Man (By Sam Raimi)');
Selecting entries
To see the entries in a table, you have to use a SELECT command. Please run the following command to see the example.
sqlite> SELECT * FROM movies;
-- Result
-- 1|Spider-Man: Into the Spider-Verse
-- 2|The amazing spider-man
-- 3|Spider-Man: Homecoming
-- 4|Spider-Man (By Sam Raimi)
The asterisk(*) indicates that we will select all columns from the table movies.
You can select entry with a certain criteria using a WHERE clause. The following command selects only entries that have "id" value less than 3.
SELECT * FROM movies WHERE id < 3;
-- Result
-- 1|Spider-Man: Into the Spider-Verse
-- 2|The amazing spider-man
Updating an entry
To update an entry, you have to use an UPDATE command. Please run the following command to see the example.
-- Change "Spider-Man (By Sam Raimi)" to "Spider-Man (Tobey Maguire)"
UPDATE movies SET "title" = 'Spider-Man (Tobey Maguire)' WHERE id = 4;
To see the result, run a select command.
SELECT * FROM movies where id = 4;
-- Result
-- 4|Spider-Man (Tobey Maguire)
Deleting an entry
To delete an entry, a DELETE command is used. Please run the following command to see the example.
DELETE FROM movies WHERE id = 4;
Adding Relationship
Add some reviews to a movie
To add comment entries to a movie, run the following command.
INSERT INTO reviews ("stars", "comment", "movie_id") VALUES
(5, 'very good movie!', 1),
(4, 'nice movie tho', 1);
If you select all reviews, you'll see the following result.
select * from reviews;
-- Result
-- 1|5|very good movie!|1
-- 2|4|nice movie tho|1
Summary
You have learnt the basics of how to use SQL database. You can use the SQL database to store structured-data. And also learn how to add relationships between models. You can manipulate data in the database using INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE/SELECT commands.
However, SQL database still have more features available. If you wish to learn more, please go the following links.